안 쓰던 블로그
Object Detection_3. 성능 평가 Metric - IOU 본문
Box를 그렸으니 원본과 얼마나 맞아 떨어지는지를 확인해야 한다
IoU: Intersection over Union
모델이 예측한 결과와 실측(Ground Truth) Box가 얼마나 정확하게 겹치는가를 나타내는 지표
$$IoU=\frac{Area of Overlap(개별 Box가 서로 겹치는 영역)}{Area of Union(전체 Box의 합집합 영역)}$$
IoU의 값이 0.4정도라면 예측이 아주 맞지 않는다
값이 0.7정도라면 나쁘지 않게 맞았고, 1에 가까울 수록 예측이 맞았다고 보면 된다
목표는 당연히 IoU값이 1에 가깝게 만드는 것
얼마 이상의 값부터 맞았다고 생각할지는 보통 0.5부터 적당히 조정한다
IoU구하기-입력인자로 후보 박스와 실제 박스를 받아서 IOU를 계산하는 함수 생성
import numpy as np
def compute_iou(cand_box, gt_box):
# Calculate intersection areas
x1 = np.maximum(cand_box[0], gt_box[0])
y1 = np.maximum(cand_box[1], gt_box[1])
x2 = np.minimum(cand_box[2], gt_box[2])
y2 = np.minimum(cand_box[3], gt_box[3])
intersection = np.maximum(x2 - x1, 0) * np.maximum(y2 - y1, 0)
cand_box_area = (cand_box[2] - cand_box[0]) * (cand_box[3] - cand_box[1])
gt_box_area = (gt_box[2] - gt_box[0]) * (gt_box[3] - gt_box[1])
union = cand_box_area + gt_box_area - intersection
iou = intersection / union
return iou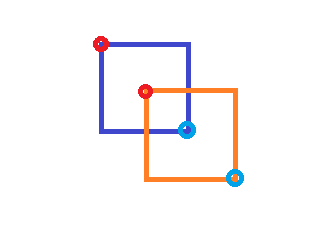
IoU공식에서 교집합 영역과 합집합 영역을 계산해야 한다
인자값 cand_box(추측 박스)와 gt_box(실제 박스)는 x1,y1,x2,y2를 갖는다
교집합 영역
두 영역의 좌상단 좌표 중 큰 값, 두 영역의 우하단 좌표 중 작은 값을 구한다
위의 그림 기준으로는 안 쪽의 빨간원, 안 쪽의 파란원이 잡힐 것이다
그렇게 x1,y1,x2,y2를 구한 뒤에 x2-x1과 y2-y1을 곱해서 넓이를 구한다
코드에서 maximum 0을 한 이유는 음수가 나오지 않도록 하기 위함이다
합집합 영역
두 영역의 넓이를 구한 뒤, 교집합 영역을 뺀다
IoU값 계산
교집합/합집합
실습을 위한 Ground Truth 박스를 정함(임의값으로 넣음)
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
# 실제 box(Ground Truth)의 좌표를 아래와 같다고 가정한다
gt_box = [60, 15, 320, 420]
default_dir = '/content/DLCV' #디폴트 디렉토리를 지정(절대경로 사용!!)
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(default_dir, 'data/image/audrey01.jpg')) #상세 파일/디렉토리 지정
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
red = (255, 0 , 0)
img_rgb = cv2.rectangle(img_rgb, (gt_box[0], gt_box[1]), (gt_box[2], gt_box[3]), color=red, thickness=2)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.show()
Region Proposal(후보 영역) 선택
import selectivesearch
#selectivesearch.selective_search()는 이미지의 Region Proposal정보를 반환
_, regions = selectivesearch.selective_search(img_rgb, scale=100, min_size=2000)
print(type(regions), len(regions))
'
IoU값 구하기
cand_rects = [cand['rect'] for cand in regions]
for index, cand_box in enumerate(cand_rects):
cand_box = list(cand_box)
cand_box[2] += cand_box[0] #너비
cand_box[3] += cand_box[1] #높이
iou = compute_iou(cand_box, gt_box)
print('index:', index, "iou:", iou)rect만 뽑아내어 너비와 높이를 계산하고, 위에서 만든 iou함수에 값을 전달하여 iou값을 구한다

정렬
cand_rects = [cand['rect'] for cand in regions if cand['size'] > 5000]
cand_rects.sort()
cand_rects5000이상의 크기인 값만 정렬 후 출력해 보면 중복값이 좀 보일 수도 있다
알고리즘이 물체가 있을만한 곳을 추측해서 선택하다보니까 중복이 나올 수 있다
최종 코드
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(default_dir, 'data/image/audrey01.jpg'))
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
print('img shape:', img.shape)
green_rgb = (125, 255, 51)
cand_rects = [cand['rect'] for cand in regions if cand['size'] > 3000]
gt_box = [60, 15, 320, 420]
img_rgb = cv2.rectangle(img_rgb, (gt_box[0], gt_box[1]), (gt_box[2], gt_box[3]), color=red, thickness=2)
for index, cand_box in enumerate(cand_rects):
cand_box = list(cand_box)
cand_box[2] += cand_box[0]
cand_box[3] += cand_box[1]
iou = compute_iou(cand_box, gt_box)
if iou > 0.5:
print('index:', index, "iou:", iou, 'rectangle:',(cand_box[0], cand_box[1], cand_box[2], cand_box[3]) )
cv2.rectangle(img_rgb, (cand_box[0], cand_box[1]), (cand_box[2], cand_box[3]), color=green_rgb, thickness=1)
text = "{}: {:.2f}".format(index, iou)
cv2.putText(img_rgb, text, (cand_box[0]+ 100, cand_box[1]+10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.4, color=green_rgb, thickness=1)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
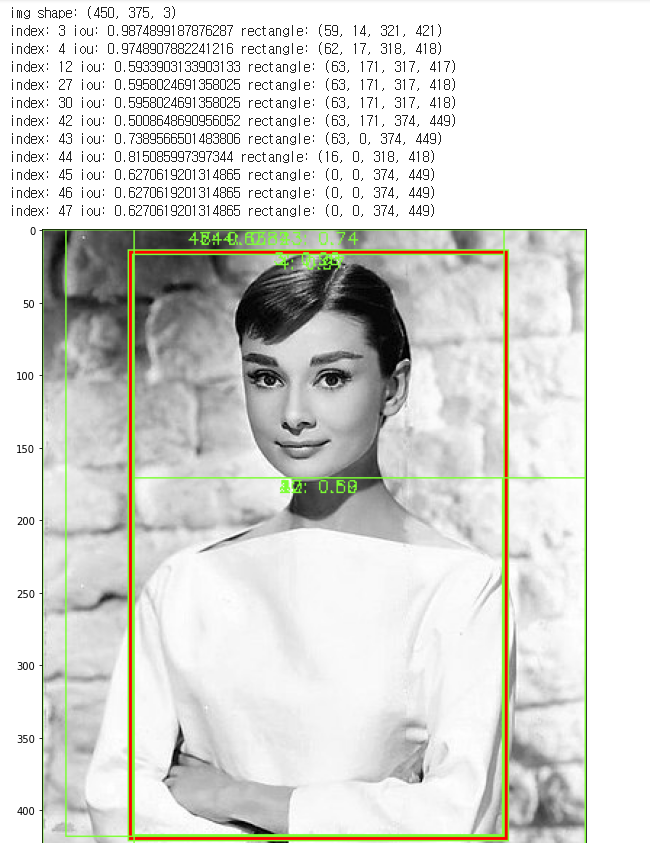
plt.show()처음에 그림을 가져오고, 그림을 출력한다
빨간색으로 실제 영역을 표시한다(임의값으로 인물을 잡음)
사이즈가 3000이상인 후보 박스들의 값을 보면서 iou값을 계산한다
iou값이 0.5이상이면 초록색으로 해당 후보 박스를 그린다
'머신러닝 > 머신러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Object Detection_5. Pascal VOC 데이터 세트 가져오기 (0) | 2021.01.17 |
|---|---|
| Object Detection_4. NMS 및 성능 평가 Metric - mAP (1) | 2021.01.17 |
| Object Detection_2. 실습 (0) | 2021.01.11 |
| Object Detection_1. 개념 (0) | 2021.01.10 |
| 구글 코랩colab 사용, 구글 드라이브에 연동 2021기준 (0) | 2021.01.10 |



